Salesforce SOAP Connector Example¶
The Salesforce SOAP Connector allows you to work with records in Salesforce, a web-based service that allows organizations to manage contact relationship management (CRM) data. You can use the Salesforce connector to create, query, retrieve, update, and delete records in your organization's Salesforce data. The connector uses the Salesforce SOAP API to interact with Salesforce.
What you'll build¶
This example explains how to use the Salesforce client to connect with the Salesforce instance and perform the create sObjects operation. Then execute a SOQL query to retrieve the Account Names in all the existing accounts. All operations are handling as SOAP messages.
-
Create an sObjects in Salesforce.
The user sends the request payload that includes sObjects (any object that can be stored in the Lightning platform database), to create a new Account object in Salesforce. This request is sent to the integration runtime by invoking the Salesforce SOAP connector API.
-
Execute a SOQL query to retrieve the Account Names in all the existing accounts.
In this example use the Salesforce Object Query Language (SOQL) to search stored Salesforce data for specific information which is created under
sObjects.
All two operations are exposed via an salesforce-soap-API API. The API with the context /salesforce has two resources
/createRecords: Creates a newAccountobject in Salesforce./queryRecords: Retrieve the Account Names in all the existing accounts in Salesforce.

The user calls the Salesforce SOAP API. It invokes the createRecords resource and creates a new account in Salesforce. Then through the queryRecords resource, it displays all the existing account details to the user.
If you do not want to configure this yourself, you can simply get the project and run it.
Configure the connector in WSO2 Integration Studio¶
Connectors can be added to integration flows in WSO2 Integration Studio. Once added, the operations of the connector can be dragged onto your canvas and added to your sequences.
Import the connector¶
Follow these steps to set up the Integration Project and the Connector Exporter Project.
-
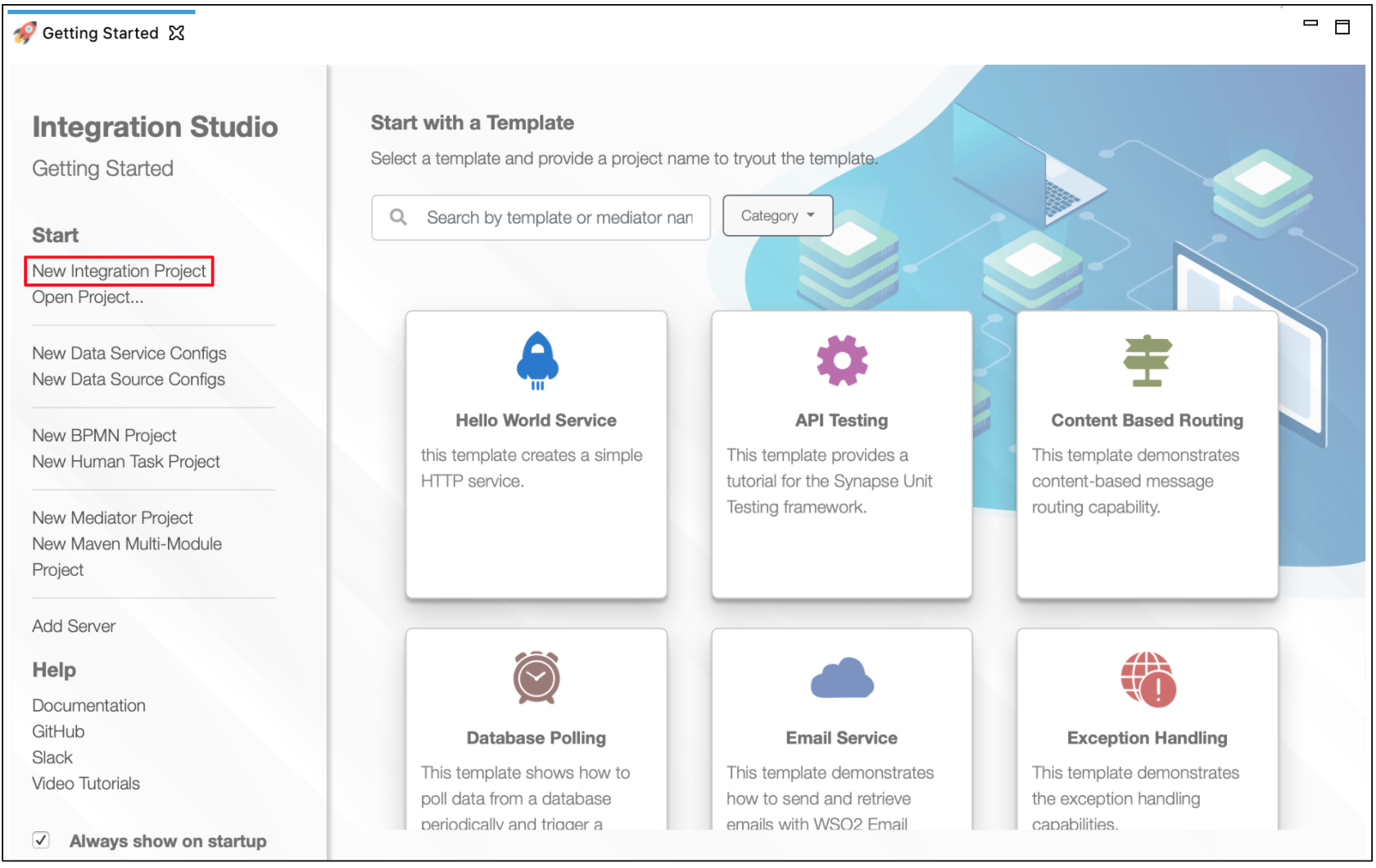
Open WSO2 Integration Studio and select New Integration Project to create an Integration Project.
-
Right-click the project that you created and click on Add or Remove Connector -> Add Connector. You will get directed to the WSO2 Connector Store.
-
Search for the specific connector required for your integration scenario and download it to the workspace.

-
Click Finish, and your Integration Project is ready. The downloaded connector is displayed on the side palette with its operations.
-
You can drag and drop the operations to the design canvas and build your integration logic.
-
Right click on the created Integration Project and select New -> Rest API to create the REST API.
Add integration logic¶
First create an API, which will be where we configure the integration logic. Right click on the created Integration Project and select, New -> Rest API to create the REST API. Specify the API name as salesforcerest and API context as /salesforcerest.

Configuring the createRecords resource¶
Now follow the steps below to add configurations to the resource.
-
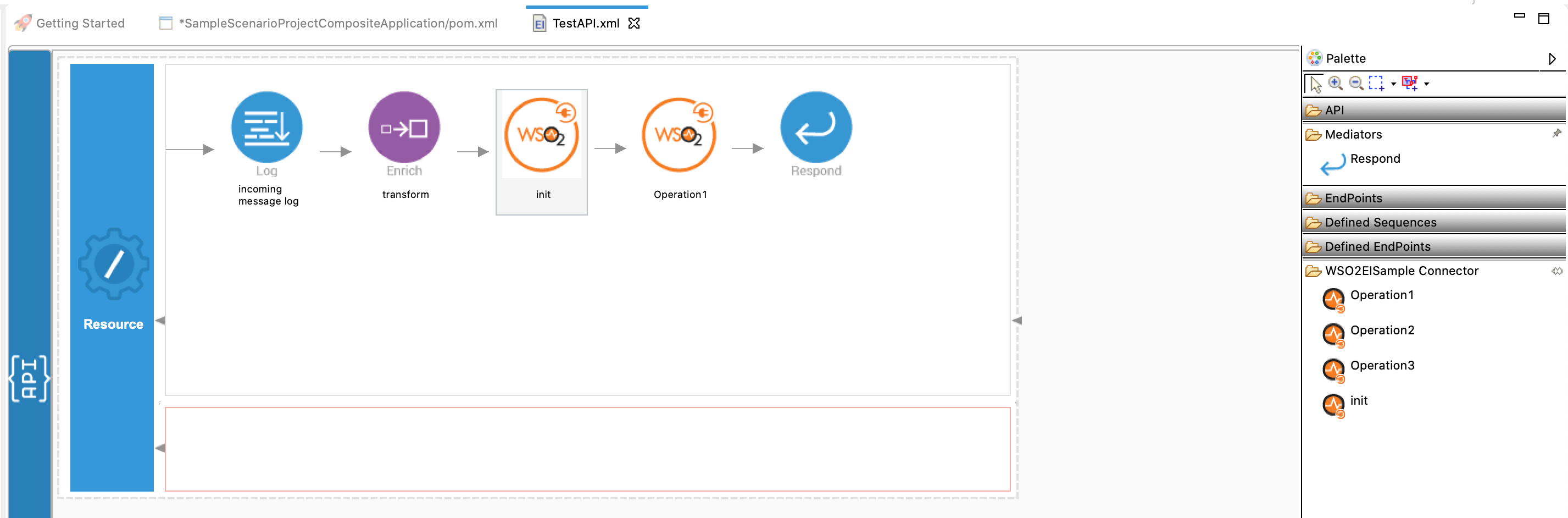
Initialize the connector.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Salesforce Connector section. Then drag and drop the
initoperation into the Design pane.
-
Add the property values into the
initoperation as shown below. Replace theusername,password,loginUrlandblockingwith your values.- username: The username to access the Salesforce account.
- password: The password provided here is a concatenation of the user password and the security token provided by Salesforce.
- loginUrl : The login URL to access the Salesforce account.
- blocking : Indicates whether the connector needs to perform blocking invocations to Salesforce. (Supported in WSO2 ESB 4.9.0 and later.)
-
-
Set up the salesforce.create operation.
-
Setup the
createconfigurations.In this operation we are going to create a
sObjectsin the Salesforce account. AnSObjectrepresents a specific table in the database that you can discretely query. It describes the individual metadata for the specified object. Please find thecreateoperation parameters listed here.- sObjectName : XML representation of the records to add.
- allowFieldTruncate : Whether to truncate strings that exceed the field length (see Common Parameters).
- allOrNone : Whether to rollback changes if an object fails (see Common Parameters).
While invoking the API, the above three parameters values come as a user input.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Salesforce Connector section. Then drag and drop the
createoperation into the Design pane.
-
To get the input values in to the API we can use the property mediator. Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical mediators icons listed under Mediators section. Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as shown bellow.
The parameters available for configuring the Property mediator are as follows:
Note: That the properties should be add to the pallet before create the operation.
-
Add the property mediator to capture the sObject
Namevalue. In this example we are going to create a new Account object using the POST method.- name : Name
- expression : //Name/text()
- type : STRING

-
Add the payload factory mediator to capture the sObject content.

-
Forward the backend response to the API caller.
When you are invoking the created resource, the request of the message is going through the
/createRecordsresource. Finally, it is passed to the Respond mediator. The Respond Mediator stops the processing on the current message and sends the message back to the client as a response.Drag and drop respond mediator to the Design view.

-
Configuring the queryRecords resource¶
-
Initialize the connector.
- You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in section 1.1 and 1.2 for setting up the
initoperation to thecreateRecordsoperation.
- You can use the same configuration to initialize the connector. Please follow the steps given in section 1.1 and 1.2 for setting up the
-
Set up the salesforce.query operation.
-
Setup the
queryconfigurations.In this operation we are going to retrieve data from an object, use
salesforce.queryand specify the following properties. If you already know the record IDs, you can use retrieve instead.- batchSize : The number of records to return. If more records are available than the batch size, you can use the queryMore operation to get additional results.
- queryString : The SQL query to use to search for records.
While invoking the API, the above two parameters values come as a user input.
-
Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical operations icons listed under Salesforce Connector section. Then drag and drop the
queryoperation into the Design pane.
-
To get the input values in to the API we can use the property mediator. Navigate into the Palette pane and select the graphical mediators icons listed under Mediators section. Then drag and drop the
Propertymediators into the Design pane as shown below. -
Add the property mediator to capture the sObject
queryStringvalue. In this example we are going to create a new Account object using the POST method.- name : queryString
- expression : //queryString/text()
- type : STRING

-
Forward the backend response to the API caller.
When you are invoking the created resource, the request of the message is going through the
/createRecordsresource. Finally, it is passed to the Respond mediator. The Respond Mediator stops the processing on the current message and sends the message back to the client as a response.Drag and drop respond mediator to the Design view.

Now you can switch into the Source view and check the XML configuration files of the created API and sequences.
create.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <api context="/salesforce" name="salesforce-soap-API" xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/createRecords"> <inSequence> <property expression="//Name/text()" name="Name" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <salesforce.init> <username>[email protected]</username> <password>eiconnectortestXXXnO9Nz4Qpiz5Us4N7ijj9zyA</password> <loginUrl>https://login.salesforce.com/services/Soap/u/42.0</loginUrl> <blocking>false</blocking> </salesforce.init> <payloadFactory media-type="xml"> <format> <sfdc:sObjects type="Account" xmlns:sfdc="sfdc"> <sfdc:sObject> <sfdc:Name>{$ctx:Name}</sfdc:Name> </sfdc:sObject> </sfdc:sObjects> </format> <args/> </payloadFactory> <salesforce.create> <allOrNone>0</allOrNone> <allowFieldTruncate>0</allowFieldTruncate> <sobjects xmlns:sfdc="sfdc">{//sfdc:sObjects}</sobjects> </salesforce.create> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence> <send/> </outSequence> <faultSequence/> </resource> <resource methods="POST" url-mapping="/queryRecords"> <inSequence> <property expression="//queryString/text()" name="queryString" scope="default" type="STRING"/> <salesforce.init> <username>[email protected]</username> <password>eiconnectortestXXXnO9Nz4Qpiz5Us4N7ijj9zyA</password> <loginUrl>https://login.salesforce.com/services/Soap/u/42.0</loginUrl> <blocking>false</blocking> </salesforce.init> <salesforce.query> <batchSize>200</batchSize> <queryString>{$ctx:queryString}</queryString> </salesforce.query> <respond/> </inSequence> <outSequence> <send/> </outSequence> <faultSequence/> </resource> </api>Get the project¶
-
You can download the ZIP file and extract the contents to get the project code.
Tip
You may need to update the value of the access token and make other such changes before deploying and running this project.
Deployment¶
Follow these steps to deploy the exported CApp in the integration runtime.
Deploying on Micro Integrator
You can copy the composite application to the <PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonapps folder and start the server. Micro Integrator will be started and the composite application will be deployed.
You can further refer the application deployed through the CLI tool. See the instructions on managing integrations from the CLI.
Click here for instructions on deploying on WSO2 Enterprise Integrator 6
-
You can copy the composite application to the
<PRODUCT-HOME>/repository/deployment/server/carbonappsfolder and start the server. -
WSO2 EI server starts and you can login to the Management Console https://localhost:9443/carbon/ URL. Provide login credentials. The default credentials will be admin/admin.
-
You can see that the API is deployed under the API section.
Testing¶
Invoke the API as shown below using the curl command. Curl Application can be downloaded from here.
-
Create a new
Accountobject in Salesforce.Sample request
curl -v POST -d '<Name>Engineers</Name>' "http://172.17.0.1:8290/salesforce/createRecords" -H "Content-Type:text/xml"Expected Response
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns="urn:partner.soap.sforce.com"> <soapenv:Header> <LimitInfoHeader> <limitInfo> <current>55</current> <limit>15000</limit> <type>API REQUESTS</type> </limitInfo> </LimitInfoHeader> </soapenv:Header> <soapenv:Body> <createResponse> <result> <id>0012x00000Am4kXAAR</id> <success>true</success> </result> </createResponse> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope> -
Retrieve the Account Names in all the existing accounts in Salesforce.
Sample request
curl -v POST -d '<queryString>select id,name from Account</queryString>' "http://172.17.0.1:8290/salesforce/queryRecords" -H "Content-Type:text/xml"
You will get a set of account names and the respective IDs as the output.What's Next¶
- To customize this example for your own scenario, see Salesforce SOAP Connector Configuration documentation for all operation details of the connector.
